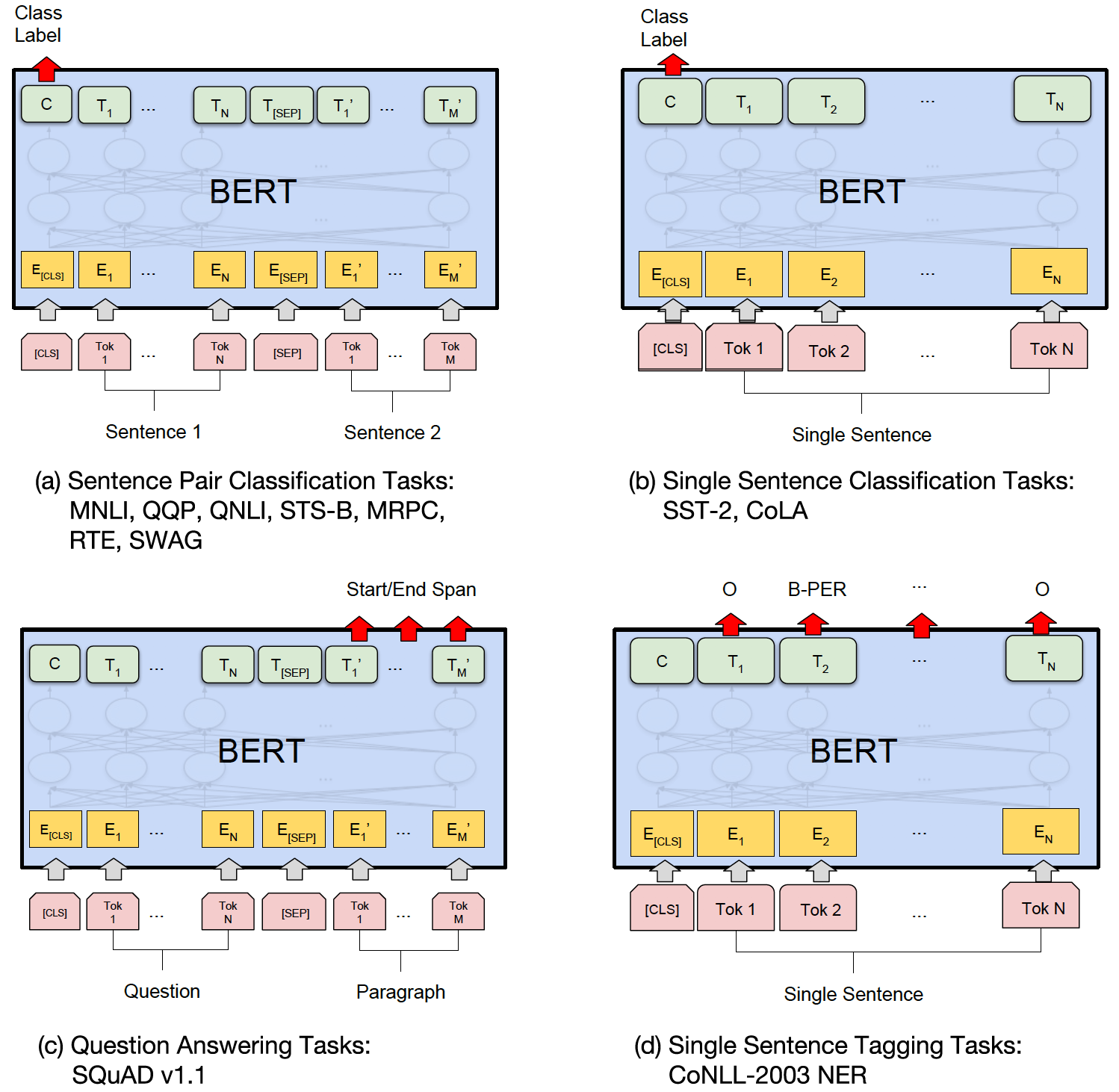
本文结构为:
- Bert网络结构
- Transformer
- Bert特点
- Bert输入与预处理
- tokenization.py
- create_pretraining_data.py
- Bert 模型代码
- modeling.py
- 预训练
- 下游任务
一, Bert网络结构
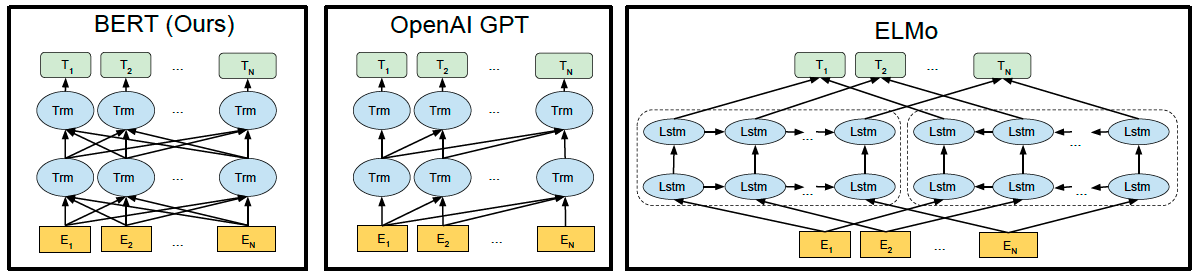
- BERT用transformer方法取代了ELMo中用LSTM提取特征的方法;
- BERT解决了GPT中单向语言模型的方法,变为双向;
- BERT采用了Fine tuning方式。(ELMo为Feature-based:将训练出的representation作为feature用于任务,词向量、句向量、段向量、文本向量都是这样的)
Bert提供了简单和复杂两个模型,对应的超参数分别如下:
- \(BERT_{BASE}\): L=12, H=768, A=12,参数总量110M;
- \(BERT_{LARGE}\): L=24, H=1024, A=16,参数总量340M;
其中,L表示网络的层数,即Transformer blocks的数量,A表示Multi-Head Attention的数量
Transformer
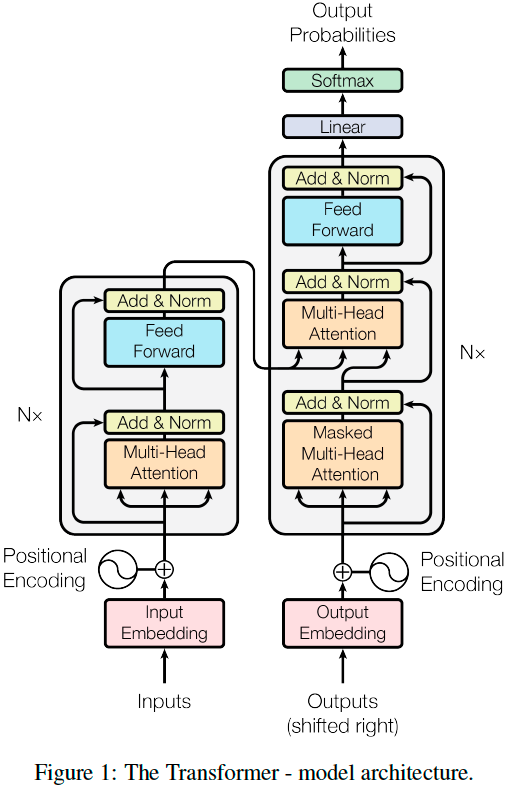
Transformer为encoder-decoder结构,如上图所示,左半部分为encoder,右半部分为decoder。
Encoder:
encoder由6个相同的layer组成,每个layer由两个sub-layer组成,分别是multi-head self-attention mechanism和fully connected feed-forward network。其中每个sub-layer都加了residual connection 和 normalisation,因此可以将sub-layer的输出表示为:
\[sub\_layer\_output = LayerNorm(x + (SubLayer(x)))\]-
Multi-head self-attention mechanism
attention可表示为:
multi-head attention是通过h个不同的线性变换对Q,K,V进行投影,最后将不同的attention结果拼接起来:
\[MultiHead(Q, K, V) = Concat(head_1, \cdots, head_h) W^o \\ head_i = Attention(QW_i^Q, KW_i^K, VW_i^V)\]Self-attention则是取Q,K,V相同。
-
Position-wise feed-forward networks
全联接层。
二, Bert特点
- Bert预训练模型的输入向量是Token Embeddings + Segment Embeddings + Position Embeddings。
- Bert训练的词向量不是完整的,而是WordPiece Embedding,因此要通过Bert模型得到英文Word Embedding要将WordPiece Embeddings转化为Word Embedding。
- 基于self-attention的Transformer结构。
- 使用Masked Language Model (masked LM)和Next Sentence Prediction (NSP)两个任务共同参与预训练过程,loss为两个任务的loss之和。
- MLM任务中,随机mask15%的token,而不是像cbow一样把每个词都预测一遍。损失函数只计算被mask掉的token的损失。mask的token中80%被替换为[MASK],10%被替代成其他单词,10%的token不做替换。
- 激活函数使用gelus。
下面从源码出发对Bert进行详细介绍。
三, Bert输入与预处理
tokenization.py
-
FullTokenizer
Bert 里的分词主要由FullTokenizer类来实现。调用BasicTokenizer和WordpieceTokenizer。前者是根据空格、标点等进行普通的分词,而后者会把前者的结果再细粒度的切分为WordPiece。
class FullTokenizer(object): """Runs end-to-end tokenziation.""" def __init__(self, vocab_file, do_lower_case=True): self.vocab = load_vocab(vocab_file) self.inv_vocab = {v: k for k, v in self.vocab.items()} self.basic_tokenizer = BasicTokenizer(do_lower_case=do_lower_case) self.wordpiece_tokenizer = WordpieceTokenizer(vocab=self.vocab) def tokenize(self, text): split_tokens = [] for token in self.basic_tokenizer.tokenize(text): for sub_token in self.wordpiece_tokenizer.tokenize(token): split_tokens.append(sub_token) return split_tokens def convert_tokens_to_ids(self, tokens): return convert_by_vocab(self.vocab, tokens) def convert_ids_to_tokens(self, ids): return convert_by_vocab(self.inv_vocab, ids) -
BasicTokenizer : 根据空格、标点等进行普通的分词,以及对汉字切分为字。
def _is_chinese_char(self, cp): """判断一个unicode字符是否是汉字""" if ((cp >= 0x4E00 and cp <= 0x9FFF) or (cp >= 0x3400 and cp <= 0x4DBF) or (cp >= 0x20000 and cp <= 0x2A6DF) or (cp >= 0x2A700 and cp <= 0x2B73F) or (cp >= 0x2B740 and cp <= 0x2B81F) or (cp >= 0x2B820 and cp <= 0x2CEAF) or (cp >= 0xF900 and cp <= 0xFAFF) or (cp >= 0x2F800 and cp <= 0x2FA1F)): return True return False def _run_strip_accents(self, text): """去除accents""" text = unicodedata.normalize("NFD", text) output = [] for char in text: cat = unicodedata.category(char) if cat == "Mn": continue output.append(char) return "".join(output) -
WordpieceTokenizer : 对英文单词切分为细粒度的WordPiece。(Bert做mask时,对属于同一个单词的WordPiece同时mask)
def tokenize(self, text): """ 使用贪心的最大正向匹配算法把一个词切分成word piece。##表示这个词是接着前面的,WordPiece切分是可逆的——我们可以恢复出“真正”的词。 """ text = convert_to_unicode(text) output_tokens = [] for token in whitespace_tokenize(text): chars = list(token) if len(chars) > self.max_input_chars_per_word: output_tokens.append(self.unk_token) continue is_bad = False start = 0 sub_tokens = [] while start < len(chars): end = len(chars) cur_substr = None while start < end: substr = "".join(chars[start:end]) if start > 0: substr = "##" + substr if substr in self.vocab: cur_substr = substr break end -= 1 if cur_substr is None: is_bad = True break sub_tokens.append(cur_substr) start = end if is_bad: output_tokens.append(self.unk_token) else: output_tokens.extend(sub_tokens) return output_tokens
create_pretraining_data.py
这块最重要的操作是函数create_instances_from_document中的内容,从单个文档中生成由TrainingInstance对象组成的instances列表,涉及到Masked Language Model (masked LM)和Next Sentence Prediction (NSP)数据准备的具体实现细节。
def create_instances_from_document(all_documents, document_index, max_seq_length, short_seq_prob,
masked_lm_prob, max_predictions_per_seq, vocab_words, rng):
"""从单个文档生成TrainingInstance对象"""
document = all_documents[document_index]
# 预留[CLS], [SEP], [SEP]的位置
max_num_tokens = max_seq_length - 3
# 增加一定的随机性,并减少pre-training和fine-tuning的差别,设置target_seq_length,但target_seq_length只是粗略目标,
# 最终的长度不一定会短于target_seq_length,但一定不会超过max_seq_length
target_seq_length = max_num_tokens
if rng.random() < short_seq_prob:
target_seq_length = rng.randint(2, max_num_tokens)
# 根据document中的sentences,获得segment_A和segment_B,(一个segment可能只有一个句子,也可能由多个句子拼接而成)
instances = []
current_chunk = []
current_length = 0
i = 0
while i < len(document):
segment = document[i]
current_chunk.append(segment)
current_length += len(segment)
if i == len(document) - 1 or current_length >= target_seq_length:
if current_chunk:
# a_end表示current_chunk中有多少segments会进入sengment_A
a_end = 1
if len(current_chunk) >= 2:
a_end = rng.randint(1, len(current_chunk) - 1)
tokens_a = []
for j in range(a_end):
tokens_a.extend(current_chunk[j])
tokens_b = []
is_random_next = False
if len(current_chunk) == 1 or rng.random() < 0.5:
is_random_next = True
target_b_length = target_seq_length - len(tokens_a)
# 随机选择其他文档
for _ in range(10):
random_document_index = rng.randint(0, len(all_documents) - 1)
if random_document_index != document_index:
break
random_document = all_documents[random_document_index]
random_start = rng.randint(0, len(random_document) - 1)
for j in range(random_start, len(random_document)):
tokens_b.extend(random_document[j])
if len(tokens_b) >= target_b_length:
break
# 确定current_chunk中未用到的句子,并将遍历该文档句子的索引重新置位到未用到的句子的位置。不浪费句子中的信息。
num_unused_segments = len(current_chunk) - a_end
i -= num_unused_segments
else:
# 使用真实的下一句
is_random_next = False
for j in range(a_end, len(current_chunk)):
tokens_b.extend(current_chunk[j])
# 选择tokens_a和tokens_b中较长的做截断,随机从头或尾做截断
truncate_seq_pair(tokens_a, tokens_b, max_num_tokens, rng)
assert len(tokens_a) >= 1
assert len(tokens_b) >= 1
tokens = []
segment_ids = []
tokens.append("[CLS]")
segment_ids.append(0)
for token in tokens_a:
tokens.append(token)
segment_ids.append(0)
tokens.append("[SEP]")
segment_ids.append(0)
for token in tokens_b:
tokens.append(token)
segment_ids.append(1)
tokens.append("[SEP]")
segment_ids.append(1)
# 随机选择15%的token做mask,80%替换成'[MASK]', 10%保持不变,10%替换成任意token
(tokens, masked_lm_positions,masked_lm_labels) \
= create_masked_lm_predictions(tokens, masked_lm_prob, max_predictions_per_seq, vocab_words, rng)
instance = TrainingInstance(
tokens=tokens,
segment_ids=segment_ids,
is_random_next=is_random_next,
masked_lm_positions=masked_lm_positions,
masked_lm_labels=masked_lm_labels)
instances.append(instance)
current_chunk = []
current_length = 0
i += 1
return instances
四, Bert 模型代码
modeling.py
class BertModel(object):
"""
BERT model ("Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers").
Example usage:
# Already been converted into WordPiece token ids
input_ids = tf.constant([[31, 51, 99], [15, 5, 0]])
input_mask = tf.constant([[1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 0]])
token_type_ids = tf.constant([[0, 0, 1], [0, 2, 0]])
config = modeling.BertConfig(vocab_size=32000, hidden_size=512,
num_hidden_layers=8, num_attention_heads=6, intermediate_size=1024)
model = modeling.BertModel(config=config, is_training=True,
input_ids=input_ids, input_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids)
label_embeddings = tf.get_variable(...)
pooled_output = model.get_pooled_output()
logits = tf.matmul(pooled_output, label_embeddings)
"""
def __init__(self, config,
is_training,
input_ids,
input_mask=None,
token_type_ids=None,
use_one_hot_embeddings=False,
scope=None):
"""
Constructor for BertModel.
"""
config = copy.deepcopy(config)
if not is_training:
config.hidden_dropout_prob = 0.0
config.attention_probs_dropout_prob = 0.0
input_shape = get_shape_list(input_ids, expected_rank=2)
batch_size = input_shape[0]
seq_length = input_shape[1]
if input_mask is None:
input_mask = tf.ones(shape=[batch_size, seq_length], dtype=tf.int32)
if token_type_ids is None:
token_type_ids = tf.zeros(shape=[batch_size, seq_length], dtype=tf.int32)
with tf.variable_scope(scope, default_name="bert"):
with tf.variable_scope("embeddings"):
# 输入的token_ids会转换成config.hidden_size(768)维的embedding
(self.embedding_output, self.embedding_table) = embedding_lookup(
input_ids=input_ids,
vocab_size=config.vocab_size,
embedding_size=config.hidden_size,
initializer_range=config.initializer_range,
word_embedding_name="word_embeddings",
use_one_hot_embeddings=use_one_hot_embeddings)
# 将token_embedding, token_type_embeddings和position_embeddings拼接共同作为模型输入。貌似三个都是使用截断正态分布生成初始化768维的向量。
self.embedding_output = embedding_postprocessor(
input_tensor=self.embedding_output,
use_token_type=True,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
token_type_vocab_size=config.type_vocab_size,
token_type_embedding_name="token_type_embeddings",
use_position_embeddings=True,
position_embedding_name="position_embeddings",
initializer_range=config.initializer_range,
max_position_embeddings=config.max_position_embeddings,
dropout_prob=config.hidden_dropout_prob)
# Transformer的encoder部分,深度为num_hidden_layers,Multi-Head Attention的数量为num_attention_heads
with tf.variable_scope("encoder"):
attention_mask = create_attention_mask_from_input_mask(input_ids, input_mask)
self.all_encoder_layers = transformer_model(
input_tensor=self.embedding_output,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
hidden_size=config.hidden_size,
num_hidden_layers=config.num_hidden_layers,
num_attention_heads=config.num_attention_heads,
intermediate_size=config.intermediate_size,
intermediate_act_fn=get_activation(config.hidden_act),
hidden_dropout_prob=config.hidden_dropout_prob,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=config.attention_probs_dropout_prob,
initializer_range=config.initializer_range,
do_return_all_layers=True)
self.sequence_output = self.all_encoder_layers[-1]
with tf.variable_scope("pooler"):
first_token_tensor = tf.squeeze(self.sequence_output[:, 0:1, :], axis=1)
self.pooled_output = tf.layers.dense(
first_token_tensor,
config.hidden_size,
activation=tf.tanh,
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(config.initializer_range))
transformer_model中激活函数使用gelus,数学表达为: \(GELU(x)=xP(X<=x)=x\Phi(x)\) Gelus其实是dropout和Relus的综合,是输入乘以一个(0,1)区间的数,这么设定使得当输入x减小的时候,输入会有一个更高的概率被dropout掉。
对于标准正太分布的 \(GELU(x)\),论文中提供了近似计算的数学公式: \(GELU(x)=0.5x(1+\tanh[\sqrt{2/\pi}(x+0.044715x^3)])\)
def transformer_model(input_tensor, attention_mask=None, hidden_size=768, num_hidden_layers=12, num_attention_heads=12,
intermediate_size=3072, intermediate_act_fn=gelu, hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1, initializer_range=0.02, do_return_all_layers=False):
"""
Multi-headed, multi-layer Transformer from "Attention is All You Need".
"""
# 因为是Multi-head attention且为self-attention, 所以需要整除
if hidden_size % num_attention_heads != 0:
raise ValueError(
"The hidden size (%d) is not a multiple of the number of attention heads (%d)"
% (hidden_size, num_attention_heads))
attention_head_size = int(hidden_size / num_attention_heads)
input_shape = get_shape_list(input_tensor, expected_rank=3)
batch_size = input_shape[0]
seq_length = input_shape[1]
input_width = input_shape[2]
# The Transformer performs sum residuals on all layers so the input needs to be the same as the hidden size.
if input_width != hidden_size:
raise ValueError("The width of the input tensor (%d) != hidden size (%d)"
% (input_width, hidden_size))
prev_output = reshape_to_matrix(input_tensor)
all_layer_outputs = []
for layer_idx in range(num_hidden_layers):
with tf.variable_scope("layer_%d" % layer_idx):
layer_input = prev_output
with tf.variable_scope("attention"):
attention_heads = []
with tf.variable_scope("self"):
attention_head = attention_layer(
from_tensor=layer_input,
to_tensor=layer_input,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
num_attention_heads=num_attention_heads,
size_per_head=attention_head_size,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=attention_probs_dropout_prob,
initializer_range=initializer_range,
do_return_2d_tensor=True,
batch_size=batch_size,
from_seq_length=seq_length,
to_seq_length=seq_length)
attention_heads.append(attention_head)
attention_output = None
if len(attention_heads) == 1:
attention_output = attention_heads[0]
else:
attention_output = tf.concat(attention_heads, axis=-1)
with tf.variable_scope("output"):
attention_output = tf.layers.dense(
attention_output,
hidden_size,
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
attention_output = dropout(attention_output, hidden_dropout_prob)
attention_output = layer_norm(attention_output + layer_input)
with tf.variable_scope("intermediate"):
intermediate_output = tf.layers.dense(
attention_output,
intermediate_size,
activation=intermediate_act_fn,
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
# Down-project back to `hidden_size` then add the residual.
with tf.variable_scope("output"):
layer_output = tf.layers.dense(
intermediate_output,
hidden_size,
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
layer_output = dropout(layer_output, hidden_dropout_prob)
layer_output = layer_norm(layer_output + attention_output)
prev_output = layer_output
all_layer_outputs.append(layer_output)
if do_return_all_layers:
final_outputs = []
for layer_output in all_layer_outputs:
final_output = reshape_from_matrix(layer_output, input_shape)
final_outputs.append(final_output)
return final_outputs
else:
final_output = reshape_from_matrix(prev_output, input_shape)
return final_output
def attention_layer(from_tensor,
to_tensor,
attention_mask=None,
num_attention_heads=1,
size_per_head=512,
query_act=None,
key_act=None,
value_act=None,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.0,
initializer_range=0.02,
do_return_2d_tensor=False,
batch_size=None,
from_seq_length=None,
to_seq_length=None):
"""
Performs multi-headed attention from `from_tensor` to `to_tensor`.
"""
def transpose_for_scores(input_tensor, batch_size, num_attention_heads, seq_length, width):
output_tensor = tf.reshape(input_tensor, [batch_size, seq_length, num_attention_heads, width])
output_tensor = tf.transpose(output_tensor, [0, 2, 1, 3])
return output_tensor
from_shape = get_shape_list(from_tensor, expected_rank=[2, 3])
to_shape = get_shape_list(to_tensor, expected_rank=[2, 3])
if len(from_shape) != len(to_shape):
raise ValueError("The rank of `from_tensor` must match the rank of `to_tensor`.")
if len(from_shape) == 3:
batch_size = from_shape[0]
from_seq_length = from_shape[1]
to_seq_length = to_shape[1]
elif len(from_shape) == 2:
if (batch_size is None or from_seq_length is None or to_seq_length is None):
raise ValueError("When passing in rank 2 tensors to attention_layer, the values for `batch_size`, "
"`from_seq_length`, and `to_seq_length` must all be specified.")
# Scalar dimensions referenced here:
# B = batch size (number of sequences)
# F = `from_tensor` sequence length
# T = `to_tensor` sequence length
# N = `num_attention_heads`
# H = `size_per_head`
from_tensor_2d = reshape_to_matrix(from_tensor)
to_tensor_2d = reshape_to_matrix(to_tensor)
# `query_layer` = [B*F, N*H]
query_layer = tf.layers.dense(
from_tensor_2d,
num_attention_heads * size_per_head,
activation=query_act,
name="query",
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
# `key_layer` = [B*T, N*H]
key_layer = tf.layers.dense(
to_tensor_2d,
num_attention_heads * size_per_head,
activation=key_act,
name="key",
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
# `value_layer` = [B*T, N*H]
value_layer = tf.layers.dense(
to_tensor_2d,
num_attention_heads * size_per_head,
activation=value_act,
name="value",
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
# `query_layer` = [B, N, F, H]
query_layer = transpose_for_scores(query_layer, batch_size, num_attention_heads, from_seq_length, size_per_head)
# `key_layer` = [B, N, T, H]
key_layer = transpose_for_scores(key_layer, batch_size, num_attention_heads, to_seq_length, size_per_head)
# Take the dot product between "query" and "key" to get the raw attention scores.
# `attention_scores` = [B, N, F, T]
attention_scores = tf.matmul(query_layer, key_layer, transpose_b=True)
attention_scores = tf.multiply(attention_scores, 1.0 / math.sqrt(float(size_per_head)))
if attention_mask is not None:
# `attention_mask` = [B, 1, F, T]
attention_mask = tf.expand_dims(attention_mask, axis=[1])
# Since attention_mask is 1.0 for positions we want to attend and 0.0 for masked positions, this operation
# will create a tensor which is 0.0 for positions we want to attend and -10000.0 for masked positions.
adder = (1.0 - tf.cast(attention_mask, tf.float32)) * -10000.0
# Since we are adding it to the raw scores before the softmax, this is effectively the same as removing these entirely.
attention_scores += adder
# Normalize the attention scores to probabilities.
# `attention_probs` = [B, N, F, T]
attention_probs = tf.nn.softmax(attention_scores)
# This is actually dropping out entire tokens to attend to, which might
# seem a bit unusual, but is taken from the original Transformer paper.
attention_probs = dropout(attention_probs, attention_probs_dropout_prob)
# `value_layer` = [B, T, N, H]
value_layer = tf.reshape(value_layer, [batch_size, to_seq_length, num_attention_heads, size_per_head])
# `value_layer` = [B, N, T, H]
value_layer = tf.transpose(value_layer, [0, 2, 1, 3])
# `context_layer` = [B, N, F, H]
context_layer = tf.matmul(attention_probs, value_layer)
# `context_layer` = [B, F, N, H]
context_layer = tf.transpose(context_layer, [0, 2, 1, 3])
if do_return_2d_tensor:
# `context_layer` = [B*F, N*H]
context_layer = tf.reshape(context_layer, [batch_size * from_seq_length, num_attention_heads * size_per_head])
else:
# `context_layer` = [B, F, N*H]
context_layer = tf.reshape(context_layer, [batch_size, from_seq_length, num_attention_heads * size_per_head])
return context_layer
五, 预训练
预训练loss为Masked Language Model (masked LM)和Next Sentence Prediction (NSP)两个任务的loss之和。这里详细可参考Bert源码,没什么特别需要解释的地方。
六, 下游任务
因为Bert预训练预料丰富模型庞大,Bert可适用的下游任务也很广泛:
- 序列标注:分词、POS Tag、NER、语义标注
- 分类任务:文本分类、情感计算
- 句子关系判断:Entailment、QA、自然语言推断
- 生成式任务:机器翻译、文本摘要等